Problem 21: RNA is an intermediary between DNA and protein.
What happens in protein synthesis?
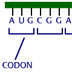
HI! RNA acts as the information bridge between DNA and protein. mRNA is the message that carries genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm. tRNA is the adaptor that reads the mRNA and brings the amino acids to the ribosomes for protein synthesis. RNA polymerase is an enzyme that makes RNA using a DNA template. Like DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase adds nucleotides in the 5' to 3' direction. Let's try an example. If Gene X begins with this T on the DNA, what is the corresponding mRNA sequence? No, this is the DNA sequence of the strand complementary to the gene. The mRNA is a complementary copy of the DNA gene but RNA uses uracil instead of thymine. mRNA is also made in the 5' to 3' direction. What happens if we introduce a point mutation —where one nucleotide is changed to another — in the DNA sequence of the gene? Messenger RNA is a copy of the genetic information on DNA. Any changes in the DNA sequence will be reflected in the mRNA sequence. The tRNA sequence does not change since tRNA does not carry the genetic information. In this case, the single DNA-base change causes the resulting protein sequence to change at one amino acid — — you'll learn more about how the genetic code is translated in the next concept. Another change that could occur in the DNA sequence is a deletion causing one or more bases to be cut out of the gene. Nothing happens to the protein. No, if the DNA sequence changes, so will the mRNA sequence and the protein sequence. The mRNA sequence has changed, so the protein sequence will change. The tRNA will no longer read the shorter mRNA, so no protein will be made. No, the tRNA can still read the mRNA. What happens to the protein coded by the mRNA of a gene if there is a 5 base pair deletion in the DNA? If there is a 5 base pair deletion in the DNA of a gene, the mRNA for the gene will be 5 base pairs shorter. Protein will still be made from this mRNA, but the protein sequence will change. In this case, the amino acid chain coded by this altered mRNA is shorter. CONGRATULATIONS!!! YOU'RE SO SMART!
rna polymerase, dna polymerase, mrna sequence, protein synthesis, dna template, messenger rna, protein sequence, complementary copy
- ID: 16492
- Source: DNALC.DNAFTB
Related Content
15510. Transcription: DNA codes for messenger RNA (mRNA), 3D animation with basic narration
Transcription factors bind to DNA, RNA polymerase begins transcribing messanger RNA (mRNA) molecule from DNA.
15480. Transcription: DNA to RNA, 3D animation with sound effects only
Transcription factors bind to DNA, RNA polymerase begins transcribing messanger RNA (mRNA) molecule from DNA.
15547. Transcription/translation - Promoters
Promoters are DNA sequences located in the 5' region adjacent to the transcriptional start site.
16528. Concept 24: The RNA message is sometimes edited.
RNA splicing removes non-coding introns and splices together exons.
16551. Concept 25: Some viruses store genetic information in RNA.
Reverse transcription is found in retroviruses.
16527. Problem 23: A gene is a discrete sequence of DNA nucleotides.
Determine the sequence of DNA.
15481. Translation: RNA to protein, 3D animation with no audio
Translation: RNA to protein, 3D animation with no audio
16470. Concept 21: RNA is an intermediary between DNA and protein.
The Central Dogma is the flow of genetic information from DNA, to RNA, to protein.
16932. Flow of Information from DNA to RNA to Protein
Dr. Roberts describes the flow of information from DNA to RNA to protein.
16494. Animation 22: DNA words are three letters long.
Several researchers crack the genetic code.