Transcription: DNA to RNA, 3D animation with sound effects only
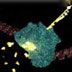
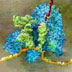
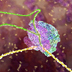
Transcription is the process by which the information in DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) for protein production. Transcription begins with a bundle of factors assembling at the promoter sequence on the DNA (in red). Here, two transcription factors are already bound to the promoter. Other proteins arrive, carrying the enzyme RNA polymerase (in blue). To initiate transcription, these assembled proteins require contact with activator proteins that bind to specific sequences of DNA known as enhancer regions. Once the contact is made, the RNA polymerase races along the DNA to transcribe the gene. (This animation with voice over found at www.dnai.org: Code > Copying the Code > putting it together > Transcription
What you are about to see is DNA's most extraordinary secret — how a simple code is turned into flesh and blood. It begins with a bundle of factors assembling at the start of a gene. A gene is simply a length of DNA instructions stretching away to the left. The assembled factors trigger the first phase of the process, reading off the information that will be needed to make the protein. Everything is ready to roll: three, two, one, GO! The blue molecule racing along the DNA is reading the gene. It's unzipping the double helix, and copying one of the two strands. The yellow chain snaking out of the top is a copy of the genetic message and it's made of a close chemical cousin of DNA called RNA. The building blocks to make the RNA enter through an intake hole. They are matched to the DNA - letter by letter - to copy the As, Cs, Ts and Gs of the gene. The only difference is that in the RNA copy, the letter T is replaced with a closely related building block known as "U". You are watching this process - called transcription - in real time. It's happening right now in almost every cell in your body.
rna polymerase,rna dna,dna rna,messenger rna,dna instructions,central dogma,chemical cousin,intake hole,genetic message,double helix,protein production,transcription factors,flesh and blood,3d animation,location code,mrna,building blocks,sound effects,strands,molecule
- ID: 15480
- Source: DNALC.DNAi
- Download: MPEG 4 Video
Related Content
15510. Transcription: DNA codes for messenger RNA (mRNA), 3D animation with basic narration
Transcription factors bind to DNA, RNA polymerase begins transcribing messanger RNA (mRNA) molecule from DNA.
16933. 3D Animation of DNA to RNA to Protein
An animation shows how the DNA genetic "code" is made into protein.
16470. Concept 21: RNA is an intermediary between DNA and protein.
The Central Dogma is the flow of genetic information from DNA, to RNA, to protein.
16551. Concept 25: Some viruses store genetic information in RNA.
Reverse transcription is found in retroviruses.
15481. Translation: RNA to protein, 3D animation with no audio
Translation: RNA to protein, 3D animation with no audio
16471. Animation 21: RNA is an intermediary between DNA and protein.
Francis Crick describes RNA and its role and Paul Zamecnick explains protein synthesis.
16938. 3D Animation of RNA Splicing
An animation of the crucial RNA editing step called splicing.
16492. Problem 21: RNA is an intermediary between DNA and protein.
What happens in protein synthesis?
1022. Pathways, Inside the nucleus
In this section learn that an activated protein is transported into the nucleus through a pore in the nuclear membrane.
15501. Translation: RNA to protein, 3D animation with basic narration
3D animation of translation: RNA to protein.