Pathways, Inside the nucleus
In this section learn that an activated protein is transported into the nucleus through a pore in the nuclear membrane.
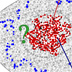
The activated protein (in pink) is transported into the nucleus through a pore in the nuclear membrane. The nucleus contains tightly wound coils of DNA (shown in green). The signal is passed to two other molecules, Fos and Jun (in yellow and pink) that team up to locate a specific gene along the DNA. Fos and jun bind the DNA, starting the process of transcription. Other proteins are then called into play that unwind and open the DNA molecule so that RNA polymerase (shown in brown) can make a copy of the genetic information. The "copy," called messenger RNA (here in light green), is packaged with a set of carrier proteins and leaves the nucleus. The cell will use this copy to make a new protein. Molecules identified: Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases: These enzymes – sometimes known as extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) – add phosphates to other proteins to activate or deactivate them. Mutations in these kinases can disrupt cell signaling and cause abnormal cell growth and proliferation. These proteins are good targets for drugs against cancer. Fos: A protein that interacts with the Jun protein to form AP-1, a transcription factor. When active, Fos and Jun bind together via a stretch of leucine amino acids that mesh like teeth in a zipper. The other ends of the proteins bind DNA to begin the transcription of growth-promoting genes. Researchers speculate that mutations in Fos and Jun may make them bind abnormally, activating target genes without responding to the usual controls. Fos is also present at high levels in cancers such as colon cancer. Jun: A protein that interacts with the Fos protein to form AP-1, a transcription factor. When active, Fos and Jun bind together via a stretch of leucine amino acids that mesh like teeth in a zipper. The other ends of the proteins bind DNA to begin the transcription of growth-promoting genes. Researchers speculate that mutations in Fos and Jun may make them bind abnormally, activating target genes without responding to the usual controls. Deoxyribonucleic acid(DNA): The molecule that carries the genetic information of a cell. DNA is composed of two strands of nucleotides that twist around each other to make the shape of a double helix. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases: These enzymes – sometimes known as extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) – add phosphates to other proteins to activate or deactivate them. Mutations in these kinases can disrupt cell signaling and cause abnormal cell growth and proliferation. These proteins are good targets for drugs against cancer. Ribonucleic acid (RNA): A molecule similar to DNA. RNA is usually single-stranded and instead of thymine has uracil as one of its four nitrogenous bases. Different types of RNA molecules are used for different purposes. For example, messenger RNA carries the information to make a protein from the nucleus to a ribosome, while transfer RNA delivers amino acids to a ribosome during protein production. RNA polymerase: An enzyme that makes a ribonucleic acid (RNA) copy of a gene during the process of transcription.
fos protein, target genes, rna polymerase, dna molecule, protein molecules, carrier proteins, messenger rna, transcription factor, colon cancer, abnormal cell growth, amino acids, nuclear membrane, cell signaling, genetic information, phosphates, mutations, nucleus, pore, coils, zipper
- ID: 1022
- Source: DNALC.IC
Related Content
16877. Cell Signals
Journey inside a cell as you follow proteins and learn about cellular interactions. This 3-D animation brings to life the inner workings of a fibroblast cell as it responds to external signals. Created by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory and Interactive Know
1023. Pathways, Making the protein
In this section learn that in the cytoplasm, the messenger RNA is released from its carrier proteins and binds to a protein assembly complex called a ribosome.
1021. Pathways, To the nucleus
In this section learn that many signaling pathways ultimately pass messages to the nucleus of a cell.
1019. Pathways, Beneath the membrane
In this section learn that the binding of growth factors outside the cell causes receptors ends to intertwine and activate each other, and once active, the modified receptor ends interact with messenger proteins.
16470. Concept 21: RNA is an intermediary between DNA and protein.
The Central Dogma is the flow of genetic information from DNA, to RNA, to protein.
1020. Pathways, A bevy of interactions
In this section learn that receptors activate each other before binding an adaptor molecule and an exchange factor.
16725. Animation 35: DNA responds to signals from outside the cell.
James Darnell explains how chemical signals turn eukaryotic genes on and off.
1024. Pathways, Releasing the protein
In this section learn that newly made proteins leave the endoplasmic reticulum wrapped in a layer of membrane called a vesicle.
959. Causes, Smoking: K-ras
This section explains how the protein produced by the K-ras gene is a tumor “activator.”
16471. Animation 21: RNA is an intermediary between DNA and protein.
Francis Crick describes RNA and its role and Paul Zamecnick explains protein synthesis.