Gallery 37: Drosophila eyeless mutant
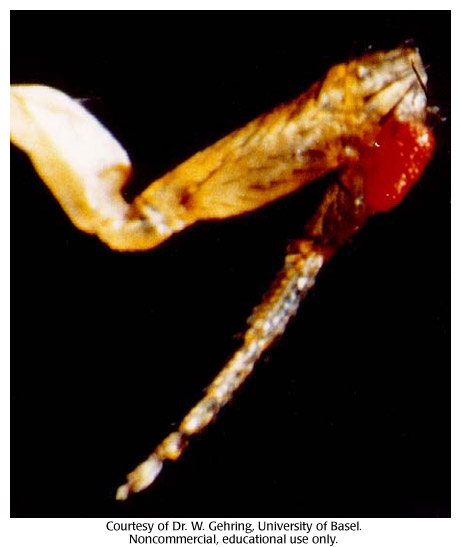
Ectopic expression of the homeotic gene eyeless causes the formation of eye structures on a Drosophila leg.
ectopic expression, homeotic gene, eye structures
- ID: 16772
- Source: DNALC.DNAFTB
Related Content
16782. Problem 37: Master genes control basic body plans.
Explore Drosophila development and embryonic protein distribution.
16759. Concept 37: Master genes control basic body plans.
Fruit fly mutaitons provided keys to understanding the molecular basis of large-scale developmental plans.
16760. Animation 37: Master genes control basic body plans.
Eric Wieschaus and Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard explain research of Drosophila's developmental stages, and Ed Lewis presents homeotic mutations.
16687. Concept 33: Genes can be turned on and off.
Organisms can regulate gene expression.
1721. 3D Gene Expression
Like all brains, insect brains have different structures that accomplish specific tasks. Dr. Josh Dubnau introduces a technique for examining gene expression in the brains of fruit flies.
1719. Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster)
The fruit fly is easy to maintain, has large numbers of offspring, and grows quickly. The fruit fly shares with humans a number of so-called “master,” or homeotic, genes.
16781. Biography 37: Edward Lewis (1918-2004)
Ed Lewis characterized one of the first homeotic mutations.
516. Expression of the DISC1 Gene
Professor David Porteous explains that DISC1 is expressed prominently in the hippocampus. More specifically, it is expressed in the mitochondria of hippocampal cells.
16735. Concept 36: Different genes are active in different kinds of cells.
Cells differentiate because specific enzymes turn genes on and off in various cell types.
15276. Genes control the structure of proteins, François Jacob
François Jacob talks about Genes control the structure of proteins