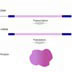
Transcription/translation -PolyA-tails - the end
The majority of eukaryotic mRNAs contain a tract of A residues at the end. These polyA-tails are not encoded in the DNA. Rather, they are added to the pre-mRNA "post-transcriptionally" (after transcription). The end of pre-mRNA is cut by a specific enzyme, and a polyA-tail is added to the mRNA strand. A signal sequence (yellow) in the 3' UTR (blue) guides the addition of the polyA-tail.
gene concept,translation 4,transcription
- ID: 15550
- Source: DNALC.DNAi
Related Content
15546. Transcription/translation - Untranslated regions
Transcription/translation
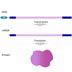
15547. Transcription/translation - Promoters
Promoters are DNA sequences located in the 5' region adjacent to the transcriptional start site.
15549. Transcription/translation - Exons and introns
In most eukaryotic genes, coding regions (exons) are interrupted by noncoding regions (introns).
15579. Transcription and translation
An image relating transcription and translation.
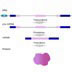
15545. Tanscription/translation - Start and stop codons
The diagram represents a single strand of DNA containing a gene, in purple. Remember this gene is "read" in the 5' to 3' direction to produce an mRNA.
2299. Transcription Factors Can Turn Genes On and Off
Doctor Anil Malhotra discusses how transcription factors can turn genes on or off, possibly leading to increased or reduced risk of illness.
2051. Gene expression - different levels in different cells
Professor Rusty Lansford explains that all genes are not expressed in the same levels in different cells; there is a lot of differential regulation.
15473. The Central Dogma: transcription and translation, James Watson
James Watson talks about the Central Dogma: transcription and translation.
1180. Cortical Asymmetry - Left Brain, Right Brain
Professor Daniel Geschwind explains that cortical asymmetry refers to differences between the right and left side of the brain. This relates to gene expression.
918. 5-HTT Gene
The 5-HTT gene has been associated with both depression and autism.