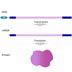
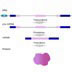
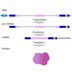
Transcription/translation - Untranslated regions
Transcription/translation
gene concept,translation 2,transcription
- ID: 15546
- Source: DNALC.DNAi
Related Content
15547. Transcription/translation - Promoters
Promoters are DNA sequences located in the 5' region adjacent to the transcriptional start site.
15549. Transcription/translation - Exons and introns
In most eukaryotic genes, coding regions (exons) are interrupted by noncoding regions (introns).
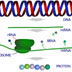
15579. Transcription and translation
An image relating transcription and translation.
15550. Transcription/translation -PolyA-tails - the end
The majority of eukaryotic mRNAs contain a tract of A residues at the end. These polyA-tails are not encoded in the DNA. Rather, they are added to the pre-mRNA "post-transcriptionally" (after transcription). The end of pre-mRNA is cut by a specific enzyme
15545. Tanscription/translation - Start and stop codons
The diagram represents a single strand of DNA containing a gene, in purple. Remember this gene is "read" in the 5' to 3' direction to produce an mRNA.
920. MET Gene
The MET gene is important to brain development, particularly in the neocortex and cerebellum.
1366. CREB2 Gene
CAMP response element-binding protein 2(CREB2) is also known as Activating Transcription Factor 2 (ATF2). CREB2 is a CREB repressor, which means it inhibits long-term memory formation.
2299. Transcription Factors Can Turn Genes On and Off
Doctor Anil Malhotra discusses how transcription factors can turn genes on or off, possibly leading to increased or reduced risk of illness.