Concept 23: A gene is a discrete sequence of DNA nucleotides.
Gene analysis take a giant leap using DNA sequencing.
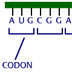
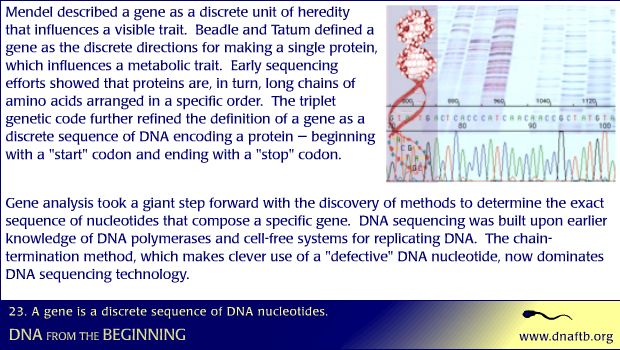
Mendel described a gene as a discrete unit of heredity that influences a visible trait. Beadle and Tatum defined a gene as the discrete directions for making a single protein, which influences a metabolic trait. Early sequencing efforts showed that proteins are, in turn, long chains of amino acids arranged in a specific order. The triplet genetic code further refined the definition of a gene as a discrete sequence of DNA encoding a protein — beginning with a "start" codon and ending with a "stop" codon. Gene analysis took a giant step forward with the discovery of methods to determine the exact sequence of nucleotides that compose a specific gene. DNA sequencing was built upon earlier knowledge of DNA polymerases and cell-free systems for replicating DNA. The chain-termination method, which makes clever use of a "defective" DNA nucleotide, now dominates DNA sequencing technology.
dna nucleotides, dna polymerases, dna nucleotide, stop codon gene, start codon, dna sequencing, discrete sequence, giant leap, amino acids, exact sequence, genetic code, mendel, triplet, proteins
- ID: 16514
- Source: DNALC.DNAFTB
Related Content
16515. Animation 23: A gene is a discrete sequence of DNA nucleotides.
Fred Sanger outlines DNA sequencing.
15545. Tanscription/translation - Start and stop codons
The diagram represents a single strand of DNA containing a gene, in purple. Remember this gene is "read" in the 5' to 3' direction to produce an mRNA.
16513. Problem 22: DNA words are three letters long.
Decode a protein.
16527. Problem 23: A gene is a discrete sequence of DNA nucleotides.
Determine the sequence of DNA.
16494. Animation 22: DNA words are three letters long.
Several researchers crack the genetic code.
16492. Problem 21: RNA is an intermediary between DNA and protein.
What happens in protein synthesis?
16036. Fred Sanger, 1975
A gene is a discrete sequence of DNA nucleotides
16491. Biography 21: Sydney Brenner (1927-2019)
Sydney Brenner showed that mRNA was the unstable intermediate that carried the message from DNA to the ribosomes.
16834. Animation 40: Living things share common genes.
Mike Wigler shows how all organisms share similar genes, called homologs.
15356. Determining the nucleotide sequences of all RNA codons, Marshall Nirenberg
Marshall Nirenberg talks about Gobind Khorana, who synthesized many of the triplets needed to finish the decoding process.