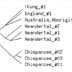
mtDNA tree all humans; Macaulay
Comparing mitochondrial genome sequences across human populations provides a means to determine the relationships among populations.
phylogenetic trees,genome sequences,common ancestor,human populations,macaulay,ancestry,eve,relationships
- ID: 16088
- Source: DNALC.DNAi
Related Content
16086. Phylogenetic Tree; Macaulay
Phylogenetic tree modern humans mitochondrial genome mtDNA relationships eve bioinformatics
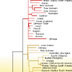
16094. Human, Neandertals, Chimpanzee
Phylogenetic relationships of modern humans, Neandertals, and chimps.
16093. Out of Africa versus Multiregionalism
Two theories are discussedfor the descendancy of modern humans: the Out Of Africa (OOA) and the Multiregionalism (MRT) theories
15165. Mitochondrial Eve, Mark Stoneking
Geneticist Mark Stoneking, one of the authors of a controversial 1987 paper on mtDNA, talks about our common female ancestor.
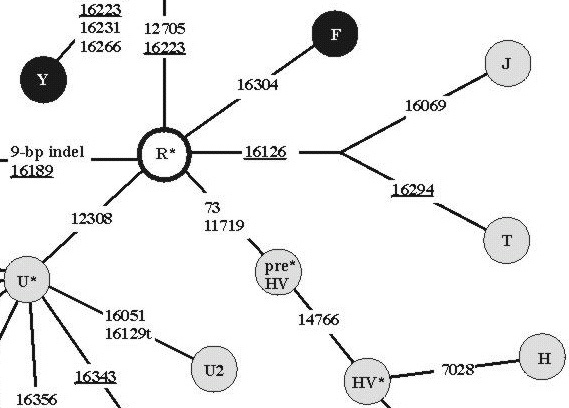
15610. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) human family tree
This illustration shows the two major mitochondrial DNA lineages. The lower branch includes only African populations. The upper branch has both African and non-African members.
16083. Human origins family tree
Meet the extended family
15592. Human - chimp common ancestor
Family tree image of human and chimp splitting off from a common ancestor.
16095. Chimp, Human, Neandertal HVR1
Variation between mtDNA (HVR1) samples from chimp, Neandertal and human.
15094. Complex story told by tracing genes back to common ancestors, Michael Hammer
Evolutionary geneticist Michael Hammer talks about the limitations of Y-chromosome research and the histories of different genes.
15971. Becoming bipedal: walking upright
Many researchers believe that the common ancestor of apes and humans was built for life in the trees. The major adaptation of the hominid branch of our family tree was bipedalism, the ability to walk on two legs. This ability allowed our ancestors to cove