Cell-free extracts
Paul Zamecnik first developed the cell-free extract system, which Marshall Nirenberg adapted to decipher the genetic code. Paul Zamecnik and Mahlon Hoagland also isolated activated tRNA, the "adaptor" that shuttled amino acids to ribsomes for incorporation into new protein chains.
protein chains,free extracts,amino acids,mahlon,genetic code,incorporation,dna,marshall
- ID: 15885
- Source: DNALC.DNAi
Related Content
15882. Breaking the code
Marshall Nirenberg and Heinrich Matthaei used poly-U mRNA in a cell-free system to make a polyphenylalanine protein chain. This showed that UUU must be the code that specifies the amino acid phenylalanine.
15347. Cell-free protein synthesis, Marshall Nirenberg
Marshall Nirenberg talks about cell-free protein synthesis.
16489. Biography 21: Paul Charles Zamecnik (1913-2009)
Paul Zamecnik developed a cell-free extract that he and Mahlon Hoagland used to study protein synthesis. They identified tRNA as the adaptor predicted by Francis Crick in his Central Dogma
16471. Animation 21: RNA is an intermediary between DNA and protein.
Francis Crick describes RNA and its role and Paul Zamecnick explains protein synthesis.
16494. Animation 22: DNA words are three letters long.
Several researchers crack the genetic code.
15349. RNA can stimulate protein synthesis, Marshall Nirenberg
Marshall Nirenberg talks about RNA can stimulate protein synthesis.
15001. Paul Zamecnik
Paul Zamecnik photo
16470. Concept 21: RNA is an intermediary between DNA and protein.
The Central Dogma is the flow of genetic information from DNA, to RNA, to protein.
16493. Concept 22: DNA words are three letters long.
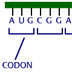
Three DNA nucleotides form a codon and specifiy amino acids.
16515. Animation 23: A gene is a discrete sequence of DNA nucleotides.
Fred Sanger outlines DNA sequencing.