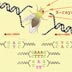
DNA nucleotide mutation
A single DNA nucleotide undergoes a "point" mutation, changing an A to a T.
dna nucleotide,point mutation,evolution
- ID: 15617
- Source: DNALC.DNAi
Related Content
16587. Concept 27: Mutations are changes in genetic information.
Some mutations are starting points for evolution, others are responsible for disease.
15557. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
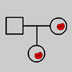
An image of a family tree depicting the occurance of single nucleotide polymorphisms.
15980. Accumulating mutations
Mutations are the grist of evolution, and have accumulated in our DNA over time. When populations separate, each group accumulates their own unique set of DNA mutations.
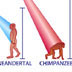
15608. Human/Neandertal/Chimp mutation evoluton tree
Mutations in our DNA can be used to trace the relationships between different populations and species.
15168. Accumulating DNA mutations through time, Mark Stoneking
Geneticist Mark Stoneking talks about the difficulties of measuring time by mutations.
16611. Problem 27: Mutations are changes in genetic information.
Use mutations to measure human evolution.
15618. mutation family tree
A hypothetical family tree useing color to illustrate different lineages. At each colored branching point, one lineage has accumulated a new mutation. The black line indicates modern times.
16588. Animation 27: Mutations are changes in genetic information.
Herman Muller induces fruit fly mutations. Seymour Benzer works with virus mutants ans proved only one nucleotide change can cause mutation.
15682. DNA nucleotides
DNA nucleotides (black letter tiles) matched in groups of two to amino acids (red letter tiles).
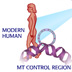
15977. Maternal inheritance
Unlike nuclear DNA, mtDNA is  inherited solely from the mother. (Mitochondria are predominantly from the motherâs egg and not from the fatherâs sperm.) Therefore, mtDNA sequences or orders of nucleotides generally remain constant over many generation