Maternal inheritance
The DNA found in mitochondria, the energy-producing organelles of cells, is often analyzed to trace evolutionary pathways. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) has a high "substitution" or mutation rate, compared with other sites in our genome. mtDNA is transmitted only from mother to child, and can be inherited intact over thousands of generations. Mutations in the mtDNA sequence can be used to reconstruct the maternal lineage of populations.
mtdna sequence,organelles of cells,maternal lineage,maternal inheritance,mutation rate,mutations,pathways,dna,populations,generations
- ID: 15977
- Source: DNALC.DNAi
Related Content
15979. A mitochondrial DNA sequence
Human mitochondrial DNA is 16,569 base pairs in length.
15978. Mitochondrial DNA: a closer look
DNA found in the mitochondrion of a cell differs in structure and is separate from the DNA found in the cell nucleus. Mitochondrial DNA, or mtDNA, exists as a circular loop of double-stranded DNA rather than the linear form found in nuclear DNA. However,
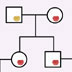
15611. mtDNA / Y chromosome pedigree, animated image
A pedigree illustrating maternal inheritance of mtDNA and paternal inheritance of the Y chromosome.
16655. Higher cells incorporate an ancient chromosome.
DNAFTB Problem 30: Trace mitochondria through Queen Victoria's decendants and solve the mystery of the Romanovs.
15178. Mitochondrial DNA and the molecular clock, Douglas Wallace
Geneticist Douglas Wallace explains a method of mapping a population's history using the mutations accumulated by its members.
15418. Mitochondrial DNA, Matt Ridley
Matt Ridley talks about Mitochondrial DNA.
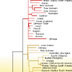
15610. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) human family tree
This illustration shows the two major mitochondrial DNA lineages. The lower branch includes only African populations. The upper branch has both African and non-African members.
15980. Accumulating mutations
Mutations are the grist of evolution, and have accumulated in our DNA over time. When populations separate, each group accumulates their own unique set of DNA mutations.
15181. Mitochondrial DNA and female lineages, Douglas Wallace
Mitochondrial DNA research pioneer Douglas Wallace speaks about mitochondrial DNA and female lineages
15975. Human and mtDNA variation
When comparing Neandertal and human mtDNA, researchers found that the differences between the sequences put Neandertals outside the range of variation of modern humans.