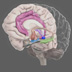
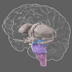
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus regulates a wide range of behavioral and physiological activities. It controls many autonomic functions such as hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sexual activity.
The hypothalamus regulates a wide range of behavioral and physiological activities. It controls many autonomic functions such as hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sexual activity. To do this, the hypothalamus integrates information from many different parts of the brain and is responsive to a variety of stimuli including light (it regulates circadian rhythms), odors (e.g. pheromones), stress, and arousal (hypothalamic neurons release oxytocin directly into the bloodstream). Other functions controlled by the hypothalamus include parenting behavior, perspiration, blood pressure, and heart rate.
hypothalamus, hypothalamic neurons, brain, autonomic functions, oxytocin, body temperature, sexual activity, perspiration, hunger, blood pressure
- ID: 2110
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
2103. Limbic System
The limbic system is a group of brain structures including the amygdala, hippocampus, and hypothalamus that are involved in processing and regulating emotions, memory, and sexual arousal.
2094. Brain Stem
The brain stem consists of a group of structures, including the pons, medulla oblongata, and midbrain. It controls autonomic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
822. The Amygdala, the Body's Alarm Circuit
The amygdala controls autonomic responses associated with fear, arousal, and emotional stimulation and has been linked to anxiety disorder and social phobias.
2206. Endocrine system - functions
Professor Bruce McEwen describes some of the key players in the endocrine system - hypothalamus, pituitary gland, adrenal cortex, sex glands, and hormones.
829. A Gene for Pain
Different mutations in a single gene, SCN9A, demonstrate how much about pain remains mysterious.
2375. Drug Addiction and Bonding
Doctor Larry Young discusses his research with prairie voles and suggests that the same neurobiological processes may underlie drug addiction and bonding.
825. A Brain Built for Fair Play
A new theory of the neuroscientific basis for the human instinct for fair play.
2378. Neuropeptides Influence Social Bonds
Doctor Larry Young explains that social personality traits are influenced by levels of oxytocin and vasopressin in the brain.
886. Background to Chronic Pain
It is estimated that more than 50 million Americans suffer from chronic pain. What is it and how is it treated?