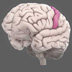
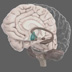
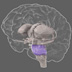
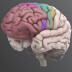
Brain Stem
The brain stem consists of a group of structures, including the pons, medulla oblongata, and midbrain. It controls autonomic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
The brain stem consists of a group of structures that lie deep within the brain, including the pons, medulla oblongata, and midbrain. It plays an important role in maintaining homeostasis by controlling autonomic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. While the brain stem can organize motor movements such as reflexes, it coordinates with the motor cortex and associated areas to contribute to fine movements of limbs and the face.
brain stem, brainstem, pons medulla, medulla oblongata, motor cortex, autonomic functions, blood pressure, maintaining homeostasis
- ID: 2094
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
2115. Somatosensory Cortex
The somatosensory cortex integrates sensory information from the body, producing a map similar to that of the primary motor cortex.
2110. Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus regulates a wide range of behavioral and physiological activities. It controls many autonomic functions such as hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sexual activity.
1147. The Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) System
Professor Trevor Robbins describes the noradrenaline system, which is highly involved in arousal.
2095. Pons
The pons is the region in the brain most closely associated with breathing and with circuits that generate respiratory rhythms.
1129. Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is part of the cerebral cortex and is the largest of the brain's structures. It is the main site of so–called 'higher' cognitive functions.
2123. Neuropathology of depression
Professor Helen Mayberg describes a network of structures linked to depression - the cingulate, hypothalamus, brainstem, and amygdala. These are influenced by frontal and parietal cortices.
838. Stem Cell Possibilities
Research continues to show that stem cells could be harnessed for therapeutic purposes.
2022. G2C 3-D Brain
The G2C Brain consists of 30 interactive 3-D structures with information on associated functions, disorders, related brain damage, case studies, and links to contemporary research.
822. The Amygdala, the Body's Alarm Circuit
The amygdala controls autonomic responses associated with fear, arousal, and emotional stimulation and has been linked to anxiety disorder and social phobias.
830. Blood-Brain Interactions
Unlike any other organ, the brain depends on continuous blood flow. If the circulation to a portion of the brain is interrupted, that area will quickly lose its ability to function.