Somatosensory Cortex
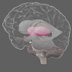
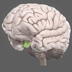
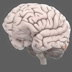
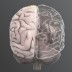
The somatosensory cortex integrates sensory information from the body, producing a map similar to that of the primary motor cortex.
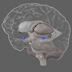
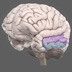
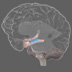
The somatosensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) receives tactile information from the body. Sensory information is carried to the brain by neural pathways to the spinal cord, brainstem, and thalamus, which project to the somatosensory cortex (which in turns has numerous connections with other brain areas). It integrates sensory information (e.g. touch, pressure, temperature, and pain, spatial attention), producing a 'homunculus map', similar to that of the primary motor cortex. Sensory information about the feet, for example, map to the medial somatosensory cortex.
somatosensory, cortex, sensory, information, brain, gyrus, brainstem, thalamus
- ID: 2115
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
2238. Perception
A overview of perception-related content on Genes to Cognition Online.
2122. Thalamus
The thalamus is heavily involved in relaying information between different brain structures. It contributes to attention, awareness, perception, attention, timing, and movement.
2119. Perirhinal Cortex
The perirhinal cortex plays an important role in object recognition and in storing information (memories) about objects. It is highly connected to other brain structures.
2113. Occipital Lobe
The occipital cortex is the primary visual area of the brain. It has different groups of neurons that separately encode color, orientation, and motion information.
2022. G2C 3-D Brain
The G2C Brain consists of 30 interactive 3-D structures with information on associated functions, disorders, related brain damage, case studies, and links to contemporary research.
2104. Amygdala
The amygdala is a complex structure adjacent to the hippocampus. The amygdala is involved in processing emotions, and fear–learning.
828. The Brain and Sleep
Researchers are using neuroimaging to look at what happens in the whole brain during sleep.
2116. Middle and Inferior Temporal Gyri
The middle and inferior temporal gyri are involved in cognitive processes, including semantic memory, language, visual perception, and sensory integration.
854. Einstein's Brain
Einstein's brain, was it different to yours?
2108. Entorhinal Cortex
The entorhinal cortex plays a major role in memory formation. Two major connections from the entorhinal area input to the hippocampus and are important to pre–processing memory information.