Frontal Lobe
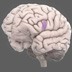
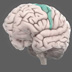
The frontal lobe is part of the cerebral cortex and is the largest of the brain's structures. It is the main site of so–called 'higher' cognitive functions.
The frontal lobes are part of the cerebral cortex and are the largest of the brain's structures. They are the main site of so–called 'higher' cognitive functions. The frontal lobes contain a number of important substructures, including the prefrontal cortex, orbitofrontal cortex, motor and premotor cortices, and Broca's area. These substructures are involved in attention and thought, voluntary movement, decision–making, and language.
frontal lobes, cerebral cortex, prefrontal cortex, cognitive functions, voluntary movement, broca, decision making, brain
- ID: 1129
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
1143. Prefrontal Cortex - Executive Functions
Professor Trevor Robbins explains that the prefrontal cortex is involved in executive functions such as planning and decision-making.
854. Einstein's Brain
Einstein's brain, was it different to yours?
832. White Matters
Only quite recently have neuroscientists begun to understand the importance of white matter, a long-neglected part of the brain.
2098. Broca's Area
Broca's area is a functionally defined structure in the left frontal lobe of most humans. It is involved mainly in producing speech, writing, and also in language processing and comprehension.
2022. G2C 3-D Brain
The G2C Brain consists of 30 interactive 3-D structures with information on associated functions, disorders, related brain damage, case studies, and links to contemporary research.
2101. Premotor Cortex
The premotor cortex is involved in preparing and executing limb movements and coordinates with other regions to select appropriate movements.
1169. COMT expression
Professor Daniel Weinberger explains that the schizophrenia candidate gene, COMT, is abundantly expressed in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex.
837. Addiction as Overlearning
The idea that drug addiction is a result of 'learning gone wild' was bolstered by several reports.
2153. Neuropathology of ADHD
Professor Philip Shaw discusses three brain areas in relation to the neuropathology of ADHD: the frontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus.
1112. Broca's Area - Primary Functions
Dr. Sukhi Shergill discusses the importance of Broca's area to generating speech.