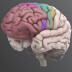
Premotor Cortex
The premotor cortex is involved in preparing and executing limb movements and coordinates with other regions to select appropriate movements.
The premotor cortex consists of a narrow region between the prefrontal and motor cortices. It is involved in preparing and executing limb movements and uses information from other cortical regions to select appropriate movements. The premotor cortex is also important for learning (imitation) and social cognition (empathy) – mirror neurons in the premotor cortex area of the macaque brain fire when the animal observes an action in others.
premotor, cortex, brain, movement, control, mirror, neurons
- ID: 2101
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
1971. Mirror neurons: brain regions
Professor Christian Keysers explains that mirror neurons can be found in many regions of the brain.
851. Developing Mirror Neurons
Mirror neurons provide an important shortcut to learning new movements.
1962. Mirror neurons: a definition
Professor Christian Keysers explains that mirror neurons in the premotor cortex respond when we perform an action and also when we see someone else perform that action. This is similar to empathy.
1972. Mirror neurons and autism
Professor Christian Keysers discusses the proposed association between autism and mirror neurons, a very hot topic in autism research.
1129. Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is part of the cerebral cortex and is the largest of the brain's structures. It is the main site of so–called 'higher' cognitive functions.
871. Mirror Neurons and Autism (2)
Abnormalities in a specific type of brain cells called mirror neurons have been associated with autism.
852. Mirror Neurons and Empathy
Empathy, research indicates, is made possible by a special group of nerve cells called mirror neurons.
1288. Neuroimaging and Autism
Neuroimaging studies of autism highlight a dysfunctional mirror neuron system, particularly in an area called the ventrolateral prefrontal cortex.
1287. Mirror Neurons - Different Types
Researchers have identified three types of mirror neurons that respond to stimuli - 1) in reaching distance, 2) outside of reaching distance, and 3) both distances.
2094. Brain Stem
The brain stem consists of a group of structures, including the pons, medulla oblongata, and midbrain. It controls autonomic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.