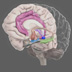
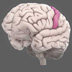
Cingulate Gyrus
An important part of the limbic system, the cingulate gyrus helps regulate emotions and pain. It is also involved in predicting and avoiding negative consequences.
An important part of the limbic system, the cingulate gyrus helps regulate emotions and pain. The cingulate gyrus is thought to directly drive the body's conscious response to unpleasant experiences. In addition, it is involved in fear and the prediction (and avoidance) of negative consequences and can help orient the body away from negative stimuli. Learning to avoid negative consequences is an important feature of memory.
cingulate gyrus, brain, pain, negative consequences, memory, limbic system
- ID: 2106
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
2103. Limbic System
The limbic system is a group of brain structures including the amygdala, hippocampus, and hypothalamus that are involved in processing and regulating emotions, memory, and sexual arousal.
2329. The Brain Rewad System - Brain Structures
Doctor Abraham Zangen discusses the key structures underlying the brain reward system, a complex neural network that includes the nucleus accumbens and hippocampus.
886. Background to Chronic Pain
It is estimated that more than 50 million Americans suffer from chronic pain. What is it and how is it treated?
1989. The neuropathology of depression and bipolar disorder
Professor James Potash discusses studies that show reductions in hippocampal volume in people with depression and abnormalities in cingulate areas in patients with bipolar disorder.
849. Hippocampus and Memory (2)
The potential gains of improving or therapeutically altering memory are compelling, but ethical considerations are imperative.
860. Anti-pain Systems
Why do women and men feel pain differently?
2107. Dentate Gyrus
The dentate gyrus is one of the few regions in the brain where adult neurogenesis has been confirmed. It may play an important role in translating neural codes for creating memories.
2123. Neuropathology of depression
Professor Helen Mayberg describes a network of structures linked to depression - the cingulate, hypothalamus, brainstem, and amygdala. These are influenced by frontal and parietal cortices.
812. The Dopamine System
Professor Trevor Robbins explains that the dopamine system is a group of cells originating in the midbrain whose function may be to prepare the brain to think, move, and anticipate rewards.
2115. Somatosensory Cortex
The somatosensory cortex integrates sensory information from the body, producing a map similar to that of the primary motor cortex.