Mental Retardation
Mental retardation: struggle, stigma, science.
Some six million Americans struggle with mental retardation, clinically deï¬ned as an IQ score below 70 to 75, signiï¬cant limitations in the skills for independent living, and appearance before adulthood. Our society has far to go in accepting and accommodating those with intellectual disabilities while scientists push ahead with the complex job of understanding how thousands of causes of mental retardation— genetic, environmental, and others — work in the brain. Much is now known about some kinds of mental retardation and the search is on for treatments that will target the underlying neurobiology. Before you read this article, try doing these exercises: 1. Coat a pair of glasses with a thin layer of Vaseline. Put the glasses on and then color a picture in a child’s coloring book. Stay inside the lines. 2. Put an oven mitt on your dominant hand. Open a box of crayons or wooden matchsticks, dump them out on a table, then pick them up one by one and put them back in the box, using the gloved hand. 3. Take a piece of rope and tie your knees together. Walk across the room. Try running. Now hop and jump. 4. Quickly read the following paragraph: Eht qaimtimg also proved that, sa wwell sa being a great humter, Cro-Wagom Nam saw a comsiberadle artist. He dah flourisheb ta a tine whem eno fo eht terridle Ice Age saw dlotting out nuch of Euroqe. He dah estadlisheb himself, fought wilb aminals rof livimg sqace, surviveb eht ditter colb, amb left beeq bown umbergroumb nenorials fo his yew fo life! 5. Sit in front of a mirror with a maze or design from a coloring book. Look in the mirror and complete the maze or trace the outline of the design as quickly as possible. Stay in the lines and trace only when looking in the mirror. 6. Put a spoon in your mouth and read the last exercise aloud. Now, imagine feeling similar frustrations every waking hour as you try to accomplish even simple tasks that society expects of you. That is the lifelong struggle against intellectual limitations and compromised living skills facing people with mental retardation. These exercises were created by a clinical social worker to let children experience impaired vision, motor skills, and speech and so begin to understand what it is like to live with a serious disability, including the group of cognitive, intellectual, and developmental disabilities clustered under the umbrella term “mental retardation.†The hope is that by helping children “walk in the shoes†of other people, those people’s differences might be accepted rather than ridiculed and that mental retardation one day might lose the harsh stigma that society has etched on it. The exercises only hint at the range of learning and physical impairments that may characterize mental retardation, a term that many people in the ï¬eld claim is itself stigmatizing and outdated. But the stigma of “intellectual disability,†as many prefer to call it, runs deeper than any label or medical term; it is rooted in a long history of societal perceptions and misconceptions that have categorized people as mentally deficient and, therefore, somehow less than fully human. Even as the stigma long stamped on mental illnesses such as depression or schizophrenia has begun to fade, perhaps as a result of wider recognition that these disorders are brain-based biological conditions, a similar public enlightenment has largely bypassed mental retardation. DISABILITY: IN THE BRAIN, IN THE PUBLIC MIND Some people in the ï¬eld, however, suggest that thinking about mental retardation as a brain disorder only reinforces the stigma. David Coulter, M.D., current president of the American Association on Mental Retardation (AAMR) says: “With mental illness, emphasizing the biological basis takes it out of the realm of ‘craziness’ or personal fault and into the realm of brain chemistry, something for which a person cannot be held personally responsible. The root of stigma in people with intellectual disabilities is based more on exclusion, perception of differences, lack of respect, and lack of a sense of value and dignity—even subhumanity. If society emphasizes the biological basis of intellectual disability, it would be making people even more different. It would only reemphasize the things that I think drive the stigma.†In 1992, the AAMR published a deï¬nition of mental retardation that reflected a new view of the condition, not as a mental illness or even a medical disorder but as a state of functioning that begins in childhood and is characterized by limitation in both intelligence and adaptive skills. “Mental retardation is not a disease,†says Coulter. “It is a statement about how a person is functioning cognitively within a social context.†Coulter believes that “The paradigm shift we introduced in 1992 was truly revolutionary in changing the way people think. What we’re saying is that, while mental retardation depends to some extent on what is going on in a person’s brain, it also depends on the demands and expectations of the environment. Maybe we, as a society, can work on all that to improve functioning.†His remark hints at a fundamental question to which diverse answers come from researchers, clinicians, and policymakers in the ï¬eld. What does it mean to talk about the possibility—even the hope—of not only treating but also curing mental retardation? In Coulter’s view, “In effect, you can talk about curing mental retardation if you could set up a person’s environment and support him or her in such a way that the person is able to function just as you and I do. Instead of thinking that it’s something you are born with and is never going to change, we can say, yes, it can change. In the right context, mental retardation could even go away.†CAUSE VERSUS CONSEQUENCE The AAMR is trying also to clarify the distinction between cause and consequence. Mental retardation can be a consequence of literally thousands of different causes, which run the gamut from genetic abnormalities or other medical conditions to social, behavioral, or educational problems. There may be more than 1,000 genetic causes alone, and yet these may account for fewer than half of cases. In as many as half of people with mental retardation, the cause is not known at all. “For every individual with mental retardation, there are some risk factors, or some combination of risk factors, that are probably causative,†Coulter says. “Sometimes it’s pretty obvious, such as in Down syndrome or fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS). But the cause is not always so obvious; it may be only suggested by factors such as premature birth, poverty, neglect, lack of adequate educational exposure, or many others.†More than six million Americans, about two or three percent of the population, have mental retardation. Down syndrome, which arises as a result of an extra copy of chromosome 21, is the most common genetic cause. Although rooted in a genetic malformation, Down syndrome is not hereditary; fragile X syndrome ranks ï¬rst in prevalence among inheritable causes, and fetal alcohol syndrome tops the list of nongenetic causes. Other known causes include exposure to environmental toxins such as mercury or lead, low birth weight, a mother’s drug use during pregnancy, prenatal or postnatal infections, head injury, severe malnutrition, and sociocultural deprivation. The common consequences of these disparate factors are abnormally low intellectual functioning (IQ scores below 70 to 75), signiï¬cant limitations in the skills necessary for independent living, and emergence before age 18—the three diagnostic criteria for mental retardation. No therapy is proven effective for mental retardation; no pill can improve intellectual functioning, nor is there a set of interventions that professionals in the ï¬eld can point to and say: “This is what your child should be getting.†With so many underlying causes and so many cases that cannot be traced to any speciï¬c cause, the search for therapies has been difï¬cult and slow. Even within a deï¬ned syndrome, there is tremendous heterogeneity in symptoms and functional capacities. For example, some people with Down syndrome are able to live independently—even achieve a college-level education—whereas others have such severe disabilities that they require full-time care and supervision. Such vastly different levels of functioning within and among the various syndromes raise a difï¬cult question: From the standpoint of underlying neurobiology, do they all have anything in common? Does any common brain pathway link mental retardation caused by a genetic disorder (such as fragile X syndrome) to mental retardation resulting from an infection in infancy or from educational impoverishment? “It is clear that mental retardation is caused by many things, each of which affects brain function in some way,†says Coulter. “But the neurobiology is different in different situations: the neurobiology of Down syndrome is different from FAS, and FAS is different from socio-cultural disadvantage, and so forth. A better understanding of the neurobiology in each of these causative conditions will allow us, eventually, to develop truly rational therapies.†CONVERGING AT THE SYNAPSE Reduced to its common denominator, all brain function—from moving a ï¬nger to solving a mathematical equation to planning one’s future—occurs at the synapse. It is at this juncture where neurons communicate, passing along neurotransmitters to activate or inhibit neighboring cells and to generate the electrical and chemical stimulation that underlies the capacity of our brain to direct the actions of every organ or system in our bodies. Intellectual capacity itself— learning, memory, reasoning, planning, and all other cognition—results from networks of individual synapses operating in concert. Thus, synapses have been a natural target of neuroscientists working to unravel the mysteries of mental retardation. Mary Blue, Ph.D., is a neurobiologist at the Kennedy Krieger Institute of Johns Hopkins University who studies Rett syndrome, autism, Down syndrome, and other genetic causes of mental retardation. She says: “The idea that ultimately mental retardation is a problem with synaptic connections in the brain is a fair statement to make—albeit admittedly vague. The synapse is where neurons talk to one another, so whenever that process is disrupted, there are going to be consequences. Ultimately, it is going to be an effect that happens at the synapse.†The problem may be one of either quality or quantity, Blue says. “If the quality of the synapse is changed, certain effects can occur. If too many synapses develop, or too few synapses, certain effects can happen.†In Rett syndrome, for example, Blue points to studies that have found about half the normal number of synapses in the cortex. In contrast, brain-imaging studies of children with autism have found that parts of the cortex are signiï¬cantly bigger than usual, an effect that seems to be most dramatic around the age of two. Scientists are trying to understand whether the increased size is due to abnormally high numbers of synaptic connections. Despite these seeming contradictions, Rett syndrome and autism also have “striking similarities,†according to Huda Zoghbi, M.D., a neuroscientist at Baylor College and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator who ï¬rst isolated the gene for Rett syndrome. So similar are these conditions that the latest edition of the International Classiï¬cation of Diseases—medical science’s bible for linking symptom to syndrome—classiï¬es Rett syndrome as a “pervasive developmental autistic spectrum disorder.†At the level of the brain, both conditions seem to involve reduced branching of dendrites, the treelike nerve ï¬bers on the receiving end of nerve transmission. In a commentary in Science in 2003, Zoghbi cited the growing evidence to support the hypothesis that both conditions are “disorders of synaptic modulation or maintenance.†SYNAPTOGENESIS GONE AWRY? Neurobiologists who study brain development have long understood that the process of creating new nerve synapses, which is called synaptogenesis, is fundamental. “We know from early development that the brain creates many more synapses, many more dendritic spines, than it can use, and one of the most critical functions in brain development is the effective pruning of all those synapses,†says Coulter. In the classic “use it or lose it†process, connections that are reinforced through experiential learning are strengthened and remain, and those not used essentially wither away. “The brain needs to have just the right number of synapses, and they need to be making just the right connections. It is just as dysfunctional to have too many as not enough,†he says. Synaptic abnormalities at either end of this spectrum are well recognized in fragile X syndrome and Down syndrome, two of the better-characterized causes of mental retardation from a neurobiological standpoint. “For a person with Down syndrome, one of the neurobiological characteristics is that he will be impoverished in terms of dendrites and therefore synapses. When the brain of a child or an adult with Down syndrome is examined at autopsy, not many branches are seen on those [dendritic] trees,†says Steven F. Warren, Ph.D., director of the Kansas Mental Retardation and Developmental Disability Research Center. “When a person is born with fragile X syndrome, the opposite problem occurs: synaptogenesis takes off in a flurry, basically without good pruning, so there are too many synapses. So either with too few synapses, or too many, mental retardation results.†All of this supports the notion that “various perturbations that affect cognitive development do so through their actions on synaptogenesis,†says Michael J. Friedlander, Ph.D., director of the University of Alabama at Birmingham Mental Retardation Research Center. Friedlander points out that such perturbations correspond to the known causes of mental retardation and include prenatal exposure to toxins or infections, inappropriate protein expression from a genetic defect, and impoverished early sensory and learning experiences. Knowing that something has gone wrong with synaptogenesis in various mental retardation syndromes is not enough, of course. Scientists want to know—and need to know, if rational therapies are to be developed—the underlying molecular mechanisms that compromise synaptic efï¬ciency and ultimately impair intellectual functioning. Some of the best progress on this front has been made in genetic syndromes that can be traced to the dysfunction of a single gene. Once a gene for a disorder has been identiï¬ed and cloned, scientists can generate animal models that carry that particular genetic defect and analyze the effects of the defect at the molecular and behavioral levels. This approach has been used effectively in Rett and fragile X syndromes. Another reason so many researchers are focused on genetic syndromes is a purely practical one, as Vanderbilt University clinical psychologist Elizabeth Dykens, Ph.D., points out: “Where research gets more bang for its buck, so to speak, both scientiï¬cally and in terms of therapeutic development, is in thinking about people who have the same underlying genetic cause for their delay [in mental development]. If, when scientists look at brain function within that cause, they see some consistent ï¬ndings, that might at least shed some light on that syndrome and how it might be treated. So that has been the track that most scientists have taken.†Understanding the genetic basis for many of the causes of mental retardation “has been the single most dramatic change†in decades, according to Roger E. Stevenson, M.D., director of Greenwood Genetic Center in Greenwood, SC. “When the genes are found, they often tell researchers what to do to cure or treat.†Stevenson, who focuses on syndromes arising from defects in speciï¬c genes on the X chromosome (X-linked mental retardation), points to three X-linked genes of particular interest to his research group for their potential in developing treatments. In each case, the defective genes encode for speciï¬c brain chemicals or hormones that are essential to some aspect of brain function. In the ï¬rst case, the essential chemical spermine is not made. In the second, a missing molecular transporter prevents creatine, an enzyme that supports energy metabolism in mitochondria, from reaching the brain. And in the third case, a transporter for a vital thyroid hormone is missing. Armed with this knowledge, researchers are now trying to determine how to replace the missing chemicals to normalize brain function. “Some people may think that this approach might involve gene manipulation or genetic engineering, or some other exotic tool genetic scientists talk and think about,†says Stevenson. “But, in fact, the likelihood is that it will be much simpler than that.†He cites the example of spina biï¬da, a condition that causes malformation of the neural tube early in prenatal development. “Spina biï¬da can be cured—or more precisely, prevented—and a healthy baby born if the mother takes folic acid before conception and in the early months of pregnancy. That is a cure: the genetics of the person have not been changed, only compensated by taking a simple B vitamin.†EXPOSING THE BIOLOGY OF FRAGILE X SYNDROME One of the most prominent examples of how the discovery of a gene for mental retardation is leading to real progress toward treatment is fragile X syndrome, which occurs in about 1 in 2,000 males and roughly half that number of females. In early March 2005, two dozen or so of the world’s leading experts in the neurobiology of fragile X syndrome gathered for the Banbury Conference, held annually at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratories on Long Island. They came armed with the latest data from their research, which ranges from pure basic science on synapse development to clinical investigations of experimental therapeutics to discoveries by pharmaceutical companies whose drugs created for other uses may be just what the doctor ordered for treating fragile X syndrome. They came to share ideas, debate, and collaborate toward a single common goal: forging a path that might one day yield an effective treatment or even a cure for a syndrome that causes moderate to severe mental retardation as well as a host of other problems. This year’s Banbury Conference was a testament to how far science has come in understanding fragile X syndrome since 1991, when the gene for it—dubbed FMR1 —was discovered. The FMR1 gene carries the code for making a protein called FMRP, and the absence of this protein causes the familiar fragile X symptoms. FMRP is likely to play many roles in normal brain physiology, roles that are still being revealed. A great deal of research attention has focused on FMRP’s speciï¬c function as an RNA-binding protein, meaning that it is essential to the crosstalk between molecular RNA and DNA, one of the fundamental mechanisms by which genes make and regulate proteins in the brain. William T. Greenough, Ph.D., a neurobiologist at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, thinks that a particular kind of protein synthesis at the dendritic spines requires FMRP. “This protein synthesis is not seen in the Fragile X knockout mouse,†he says. (The fragile X knockout mouse is bred speciï¬cally to lack the FMR1 gene.) Because new protein synthesis is known to be a requirement for learning and memory, experts believe FMRP is a key player in this process. One of the cardinal neurobiological features of fragile X syndrome, as evidenced both by examination of brain tissue at autopsy and by analysis of rodent and fly models of the condition, is abnormal dendritic spines on neurons in various parts of the brain. The spines essentially appear immature; scientists see more long, skinny spines and correspondingly fewer short, fat spines, which is how mature spines should look. In addition, a greater density of dendritic spines is found in the fragile X brain, even well past sexual maturity, when spines in the normal brain have been pruned back substantially from a peak density early in development. These discoveries, reported by Greenough and several other research groups, support the idea that fragile X syndrome may result from a failure of normal developmental synapse maturation and pruning. But the question remains: How does the absence of FMRP interfere with normal synaptogenesis? A leading hypothesis comes from Mark Bear, Ph.D., a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator now at Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Based on his research on synaptic plasticity, Bear now believes that without FMRP, synaptic connections are weakened, a process called long-term depression (LTD). The cause appears to be excessive signaling by a subclass of receptors for the neurotransmitter glutamate. Glutamate, the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain, is known to play important roles in learning and memory, and problems with its regulation have been implicated as a potential mechanism in several forms of mental retardation. While at Brown University several years ago, Bear became interested in FMRP because of this protein’s role in cognition. He and a graduate student in his laboratory at the time, Kimberly Huber, Ph.D., who now runs her own lab at University of Texas-Southwestern, began investigating how the absence of FMRP affected LTD. Bear and Huber initiated their experiments based on the hypothesis that LTD would be decreased in the absence of FMRP. “The result was exactly the opposite of what we expected,†Bear recalls. Convinced that something had gone wrong, he sent Huber back to the laboratory to repeat the experiments. When the result was the same, “We had no choice but to accept the ï¬nding,†says Bear. FMRP seemed to essentially release the brakes on glutamate activation by this important class of receptors. “The data clearly showed that long-term depression is exaggerated in the absence of the fragile X protein,†Bear says. Intrigued, Bear and his team continued on to investigate how the consequences of the lack of FMRP might be linked to fragile X symptoms. More and more evidence accumulated that seemed to explain everything from cognitive impairment to seizures to sensory hyperarousal and anxiety to loose bowel movements—all symptoms of fragile X syndrome. Bear’s theory about the role of the glutamate receptors has since been a focus of research in laboratories worldwide and has become well accepted as a key piece of the molecular puzzle underlying fragile X syndrome, even as scientists continue to work out the details. Most important, as Bear writes in a review now in press, the theory “suggests a sound scientiï¬c rationale for the treatment of fragile X syndrome. If symptoms of fragile X syndrome arise from excessive signaling...then it should be possible, in principle, to treat them with drugs that inhibit the receptors or the downstream intracellular signals they initiate.†Some groups are now trying to do this. Several big pharmaceutical companies, including Hoffman-LaRoche, Merck, and Novartis, have active drug discovery programs seeking inhibitors of the glutamate receptors, not because they are seeking a treatment for fragile X syndrome per se, but because of the potential that such drugs might be useful in other, more lucrative markets, such as anxiety and cognitive dysfunction. Sention, Inc., a small biotech ï¬rm cofounded by Bear, has recently licensed a family of glutamate receptor antagonists from Merck and is developing the compounds for clinical testing in people with fragile X syndrome. The potential problem with this approach is common to the development of drug compounds that target any receptor that has many physiologic functions in the brain: the adverse effects could be signiï¬cant. For this reason, many researchers are studying signaling pathways downstream from the receptor to uncover the particular steps unique to fragile X syndrome. Ivan Jeanne Weiler, Ph.D., a neurobiologist at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, presented data at the Banbury Conference that show just how complex this pathway is. Figuring out which piece of the maze to target is no simple task but one on which many basic scientists are now focusing. The struggle to capitalize on the new molecular understandings of fragile X syndrome to develop therapies is a case study in how basic science ï¬ndings can open doors to therapeutic discovery, and it illustrates the immensity of the task of developing pharmaceuticals for mental retardation. Even though similarities may exist among syndromes, each genetic or environmental cause of mental retardation almost certainly has its own set of molecular mechanisms, which may or may not be shared by other syndromes. A pill that might work for fragile X syndrome might not be applicable to any other syndrome—or it might be. Scientists just don’t know yet. WHAT DOES TREATMENT MEAN? In the end, it seems highly unlikely that a single drug compound will be the answer to mental retardation. Much of the focus on treatment of mental retardation has been and will continue to be compensatory: interventions that seek to modify problem behaviors or compensate for intellectual disabilities. “Treatment per se is not going to be a case whereby we can say, ‘Here’s a pill that will make everything all right,’ †says Vanderbilt’s Dykens. “Rather, it is a question of what interventions can we offer the families, children, or adults in terms of supporting them in their environment to have them function at their best. It is a complicated issue that depends on both the age of the person and his level of functioning.†Some of the more succesful interventions are targeted programs to help people with speciï¬c deï¬cits, such as language, as well as more holistic approaches that aim for an overall enrichment of a child’s environment. Over the years, a few researchers have published encouraging results of such interventions in speciï¬c syndromes, notably autism and Down syndrome, but hard data to support various approaches are still largely lacking, experts say. More rigorous investigations are under way. The concept that enriching a child’s environment can have an effect on brain development goes back to a landmark series of animal studies by Greenough and colleagues that began in the 1980s and have been repeated and extended by various groups since. In them, Greenough has shown that mice raised in cages ï¬lled with toys and exercise wheels developed signiï¬cantly more synaptic connections and performed better on learning tasks than mice raised in standard cages. His team has shown also that such “complex environments†increase the thickness of myelin in the animals’ brains, which is the insulating layer of fat around nerve ï¬bers that enhances nerve transmission. Salk Institute neurobiologist Fred Gage, Ph.D., has shown that animals raised in toy-ï¬lled cages with plenty of opportunity for experiential learning have increased rates of neurogenesis (the birth and survival of new neurons) in the hippocampus, a brain structure important to learning and memory. This line of research “is exciting in terms of its implications for how the environment can affect learning and adaptive behavior in mice and rats and, potentially, for getting a sense of how one’s environment and brain interact to make things better or worse,†says Kansas’s Warren. “The Greenough research can be seen as a good example of the notion that enriched environments can make a big difference early on in neural development, particularly if they are incorporated early in development.†Warren believes that intervening early in children with mental retardation “has the potential to make a difference.†But, he cautions, “We are very early in understanding the true potential, or even what we mean when talking about early intervention. Most of what we do in terms of behavioral interventions in the United States and most of the world is probably at so low a dose, when compared to a drug, that is is unlikely to have much of an effect.†This notion becomes clear, Warren continues, when one considers that, after the first few months of life, a normal infant is awake roughly 100 hours a week, and virtually all that time is spent working on language and communication, social interaction, and motor development, just by the nature of what infants do normally. “Standard interventions in very young children typically entail one or two hours a week of an intervention whose effectiveness is just not proven. We could make a good argument that the ‘dosage’ is just too low,†he says. PROGRESS AND PROMISE This perspective implies that, in most cases, the typical child with an intellectual disability is not getting nearly the optimal level of support and intervention. Yet, considering that just 40 years ago, children with mental retardation were essentially shipped off to an institution, to live out their lives with minimal care and little hope for a better life, that progress is being made. In the final analysis, san many experts, the responsibility for providing for people with mental retardation – and for ending the stigmatization of mental retardation- belongs to society at large, not just to scientists. “It is a totally different situation today,†says AAMR President David Coulter. “Now when a child is diagnosed with a developmental disability, the trend is to ask, ‘What can we do to help this person function better? What kinds of supports and services need to put in place?’ Good scientific evidence exists to support the notion that people with essentially all degrees of mental retardation can function and will improve in a community-based setting if they are provided with the support and services they need.â€
mental, retardation, fragile x, diability, brain, synapse, cognition,
- ID: 865
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
15945. What is Fragile X?
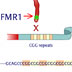
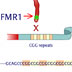
The FMR1 gene produces a protein involved in making cellular connections in the brain.
2371. Autism - A Synapse-Opathy
Doctor Gul Dolen defines synapse-opathies as disease where the synapse is the part of the brain that is disrupted. Fragile X and autism are examples.
15898. Fragile X syndrome
The FMR1 gene produces a protein involved in making cellular connections in the brain. If this gene carries many repeats of the nucleotides CGG at one end, it is deactivated. People with this mutation display mental impairments or retardation. Fragile X s
15946. What causes Fragile X?
The FMR1 gene produces a protein involved in making cellular connections in the brain. If this gene carries many repeats of the nucleotides CGG at one end, it is deactivated. People with this mutation display mental impairments or retardation. Fragile X s
2365. Fragile X Syndrome - A Cause and Cure?
Doctor Gul Dolen explains that Fragile X syndrome can be considered a disorder of plasticity, mediated by metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors, and potentially treatable with pharmaceuticals.
2363. Fragile X Syndrome
Doctor Gul Dolen describes the key characteristics of Fragile X syndrome, which can include problems with language, mental retardation, and symptoms of autism.
842. Mutations and Disorders
Sometimes chunks of DNA rearrange themselves, making them genetically unstable and prone to error.
1367. DLG3 Gene
Discs, large homolog 3 (DLG3) is a gene associated with learning and memory. DLG3 encodes synapse-associated protein 102 (SAP102).
2367. Biochemical Treatments for Autism?
Doctor Gul Dolen discusses how new biochemical treatments for Fragile X Syndrome may be used to treat autism.
550. The Neural Code
Cognitive information is encoded in patterns of nervous activity and decoded by molecular listening devices at the synapse. Professor Seth Grant explains how different patterns of neural firing are critical to cognition.