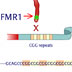
Fragile X syndrome
The FMR1 gene produces a protein involved in making cellular connections in the brain. If this gene carries many repeats of the nucleotides CGG at one end, it is deactivated. People with this mutation display mental impairments or retardation. Fragile X syndrome is the most common cause of inherited mental retardation.
fragile x syndrome,fmr1 gene,cellular connections,mental impairments,fragile x,cgg,mental retardation,mutation,protein,brain
- ID: 15898
- Source: DNALC.DNAi
Related Content
15945. What is Fragile X?
The FMR1 gene produces a protein involved in making cellular connections in the brain.
15946. What causes Fragile X?
The FMR1 gene produces a protein involved in making cellular connections in the brain. If this gene carries many repeats of the nucleotides CGG at one end, it is deactivated. People with this mutation display mental impairments or retardation. Fragile X s
865. Mental Retardation
Mental retardation: struggle, stigma, science.
2363. Fragile X Syndrome
Doctor Gul Dolen describes the key characteristics of Fragile X syndrome, which can include problems with language, mental retardation, and symptoms of autism.
842. Mutations and Disorders
Sometimes chunks of DNA rearrange themselves, making them genetically unstable and prone to error.
881. Hotspot for Autism Genes
Several lines of research are converging to show how opposing genetic pathways can lead to autism.
2365. Fragile X Syndrome - A Cause and Cure?
Doctor Gul Dolen explains that Fragile X syndrome can be considered a disorder of plasticity, mediated by metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors, and potentially treatable with pharmaceuticals.
2368. MGluRs and Treating Different Autisms?
Doctor Gul Dolen explains that there are many single-gene disorders on the autism spectrum, which may or may not respond to mGluR-related treatment.
2364. Fragile X Syndrome - Inheritance
Doctor Gul Dolen explains that Fragile X syndrome is not a mendelian disorder, because the inheritance pattern in slightly different.
2371. Autism - A Synapse-Opathy
Doctor Gul Dolen defines synapse-opathies as disease where the synapse is the part of the brain that is disrupted. Fragile X and autism are examples.