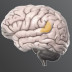
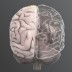
Corpus Callosum
The corpus callosum consists of a large bundle of fibers connecting the right and left hemispheres of the brain. Each hemisphere controls movement in the opposite side of the body.
The corpus callosum consists of a large bundle of fibers connecting the right and left hemispheres of the brain. Each hemisphere controls movement in the opposite (contralateral) side of the body and can also specialize in performing specific cognitive and perceptual functions. The corpus callosum allows information to move between hemispheres and is therefore a very important integrative structure.
corpus, callosum, hemispheres. lateralization, fibers, brain
- ID: 2097
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
831. Glial Communication
New avenues of scientific exploration directed at glia.
2156. Neuropathology of attention
Professor Philip Shaw discusses research that indicates a pattern of right-hemisphere dominance for attention in the mature brain.
1998. Wernicke's Area
Wernicke's area is a functionally defined structure that is involved in language comprehension.
832. White Matters
Only quite recently have neuroscientists begun to understand the importance of white matter, a long-neglected part of the brain.
853. History of Neuroscience
The evolution of ideas about brain function.
891. Neuroprotection - Protecting the Brain
Developing a safe and effective therapy to protect the brain after a stroke, a process known as neuroprotection, represents a major unsolved challenge for researchers.
884. Background to Autism
Autism is a disorder in brain development that becomes apparent in earliest childhood. It is defined by problems in socialization, communication, and repetitive behaviors.
2022. G2C 3-D Brain
The G2C Brain consists of 30 interactive 3-D structures with information on associated functions, disorders, related brain damage, case studies, and links to contemporary research.
854. Einstein's Brain
Einstein's brain, was it different to yours?
16636. Gallery 29: Electron micrograph of chromatin
Electron micrograph of the 10-nm fiber.