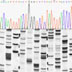
DNA sequencer

An image of a DNA sequencer.
dna sequencer
- ID: 15573
- Source: DNALC.DNAi
Related Content
15657. Outputs from DNA sequencing
Image of outputs from DNA sequencing: automated (top) and manual (bottom).
15567. DNA sequence
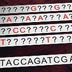
Early sequencers used four different reactions to determine the placement of each of DNA's four bases - known as A, C, T & G - in the sequence.
15981. DNA variations
A DNA fingerprint is a profile of a person's inherited DNA variations, specifically repeated sequences
15575. Human figure within DNA tunnel
The finished sequence of the human genome was published in April, 2003.
15609. DNA mutation
Multiple mutations at the same position in a DNA sequence can confound calculations of evolutionary time.
15927. Isolating DNA to make human insulin
Walter Gilbert's group tried to isolate the human insulin DNA sequence using the rat insulin DNA sequence.
15505. Synthesizing human insulin using recombinant DNA, 3D animation with no audio
Synthesizing human insulin using recombinant DNA, 3D animation with no audio
15912. Sequencing DNA
Techniques to read the sequence of DNA, letter by letter, have been available since the 1970s. However, the massive task of sequencing the three billion basepairs of the human genome required machines that could read and interpret the data.
15891. DNA sequencing game, interactive 2D animation
DNA sequencing interactive game. Reconstruct a piece of DNA using the fragments above. We've given you the first piece. You do the rest...
15922. Early DNA sequencing
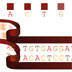
Two sequencing techniques were developed independently in the 1970s. The method developed by Fred Sanger used chemically altered "dideoxy" bases to terminate newly synthesized DNA fragments at specific bases (either A, C, T, or G). These fragments are th