Long- and Short-term Memory Differences (2)
Professor Seth Grant explains that long-term memories are created when the synapse sends a signal to the nucleus to activate certain genes.
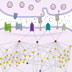
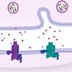
Long-term memory and short-term memory differ by the kinds of stimulation that nerve cells endure to establish those forms of learning and memory. The stimulation that produces short-term memory results in only local biochemical changes at the synapse, but the stimulation, which is usually a stronger stimulation that leads to long-term memory, not only activates the synapse but sends a signal from the synapse all the way to the nucleus where it turns on genes that then change the expression of different proteins encoding the long-term memory.
long, short, term, memory, ltm, stm, biochemical, biochemistry, synapse, nucleus, gene, protein, learning, seth, grant
- ID: 1217
- Source: DNALC.G2C
- Download: Windows Media Video Theora Video MPEG 4 Video
Related Content
550. The Neural Code
Cognitive information is encoded in patterns of nervous activity and decoded by molecular listening devices at the synapse. Professor Seth Grant explains how different patterns of neural firing are critical to cognition.
1212. NMDA Receptors and Learning (1)
Professor Seth Grant explains that NMDA receptors are important to forming memories - if we block NMDA receptors, we can block learning.
1208. Long-term Potentiation
Professor Seth Grant explains that long-term potentiation is based on the principle that synapses become stronger with experience.
1284. Local Synaptic Changes During LTM
Professor Eric Kandel discusses changes in synapse structure during long-term memory. Research indicates these changes are synapse-specific and not neuron-wide.
1210. Long-term Potentiation and Learning
Professor Seth Grant discusses the complicated relationship between long-term potentiation and learning/memory.
551. Fly School
The processes used by humans to perform certain forms of learning are the same as those in many other species. Even the humble fruit fly is an excellent model of how genes affect our ability to learn.
1279. Long- and Short-term Memory Differences (1)
Professor Eric Kandel compares short-term memory, which involves the alteration of pre-existing proteins, and long-term memory, which involves new protein synthesis.
1213. PSD-95 and Learning
Professor Seth Grant highlights PSD95 as an important example of a protein associated with a neurotransmitter receptor that affects learning.
1403. SAP102 - Sanger Institute Research
Genes to Cognition researchers discover a genetic basis for higher mental functions that provides new insights into autism and learning disability.
1277. Molecules for Memory
Communication in brain cells is guided by interactions between genes and biochemicals at the synapse. These interactions can lead to the formation of new synapses.