What causes Neurofibromatosis 1?
NF1 is a large gene that encodes three slightly different neurofibromin proteins, found in nerve and muscle tissues. These proteins act as part of a cell's signalling pathway and help to regulate cell growth and repair. Mutations in the NF1 gene can disrupt the function or production of neurofibromin proteins, leading to tumor growth in bones and the peripheral nervous system.
nf1 gene,muscle tissues,peripheral nervous system,nerve and muscle,tumor growth,proteins,mutations,chromosome,pathway,bones
- ID: 15960
- Source: DNALC.DNAi
Related Content
15959. What is Neurofibromatosis 1?
NF1 is a large gene that encodes three slightly different neurofibromin proteins, found in nerve and muscle tissue
15903. Neurofibromatosis 1
NF1 is a large gene that encodes three slightly different neurofibromin proteins, found in nerve and muscle tissues.
15962. What causes neurofibromatosis 2?
The NF2 gene produces a protein, called merlin, in the schwann cells that wrap around the axons of nerve cells. Merlin is a tumor suppressor protein, involved in regulation of the cell's activities. If the merlin protein is mutated, the schwann cells can
15961. What is neurofibromatosis 2?
The NF2 gene produces a protein, called merlin, in the schwann cells that wrap around the axons of nerve cells.
15904. Neurofibromatosis 2
The NF2 gene produces a protein, called merlin, in the schwann cells that wrap around the axons of nerve cells.
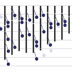
868. Candidate Genes for Schizophrenia
An interactive chromosome map of the genes and loci associated with schizophrenia.
15957. What is muscular dystrophy?
The DMD gene codes for a large protein called dystrophin that is necessary for muscle cells to maintain their shape.
15958. What causes muscular dystrophy?
The DMD gene codes for a large protein called dystrophin that is necessary for muscle cells to maintain their shape.
1018. Pathways, At the cell surface
In this section learn that a signaling pathway begins with the arrival of a chemical signal – such as a hormone or growth factor – at the cell surface.
15896. Duchenne muscular dystrophy
The DMD gene codes for a large protein called dystrophin that is necessary for muscle cells to maintain their shape.