What is cystic fibrosis?
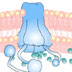
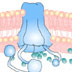
The CFTR gene encodes a protein that transports sodium and chloride (salt) ions in the body. Mutations to this gene can cause cystic fibrosis, the most common fatal genetic disorder in the United States. A defective CFTR gene cannot transport the ions, resulting in the production of thick mucus that builds up and clogs the lungs and pancreas.
salt ions,thick mucus,fatal genetic disorder,cystic fibrosis,cftr gene,ions in the body,pancreas,chromosome,mutations,lungs,sodium,protein,united states
- ID: 15941
- Source: DNALC.DNAi
Related Content
15942. What causes cystic fibrosis?
The CFTR gene encodes a protein that transports sodium and chloride (salt) ions in the body
15895. Cystic fibrosis
The CFTR gene encodes a protein that transports sodium and chloride (salt) ions in the body.
16854. Problem 40: Living things share common genes.
Find a cystic fibrosis protein function using bioinformatics to study homologs in model organisms.
15902. Marfan syndrome
Mutations in the FBN1 or fibrillin gene on chromosome 15 cause a genetic disorder called Marfan syndrome.
15955. What is Marfan syndrome?
Mutations in the FBN1 or fibrillin gene on chromosome 15 cause a genetic disorder called Marfan syndrome.
15956. What causes Marfan syndrome?
Mutations in the FBN1 or fibrillin gene on chromosome 15 cause a genetic disorder called Marfan syndrome. The misshapen protein from the mutated gene weakens the tendons, ligaments and other connective tissues in the body.
829. A Gene for Pain
Different mutations in a single gene, SCN9A, demonstrate how much about pain remains mysterious.
15068. Gene therapy (somatic cell), Mario Capecchi
Mario Capecchi talks about the possibility of correcting genetic defects.
954. Causes, Smoking, all sections
This section explains that lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States and it is almost entirely preventable, since the vast majority of cases are due to cigarette smoking.
969. Causes, Inheritance
All cancers are genetic, in that cancers are caused by genetic mutations in genes that lead to malignancy.