Temporal Lobe Hallucinations
Dr. Sukhi Shergill discusses the role the temporal lobe plays in hallucinations.
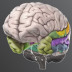
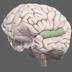
The temporal lobe is also very interesting during hallucinations. As you’d expect when people have the experience of hearing voices, when we do imaging studies, looking at their brains, the hearing part of their brains, the Wernicke's area of the the temporal lobe is working over time, working very hard. So when people do have the experience of hearing voices, it seems to be very similar to the experience of you and I hearing the voice where the same brain area would be active.
temporal, lobe, hallucination, auditory, voices, sukhi, shergill
- ID: 1114
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
1113. Broca's Area and Hallucinations
Dr. Sukhi Shergill explains that Broca’s area is active during auditory hallucinations in schizophrenia.
1118. Hallucinations - Olfactory, Visual, and Somatic
Dr. Sukhi Shergill describes the different types of hallucinations schizophrenic patients can experience.
1115. Hallucinations - Content (1)
Dr. Sukhi Shergill examines whether the content of hallucinations is important.
1116. Hallucinations - Inner Speech
Dr. Sukhi Shergill describes some of the problems schizophrenic patients experience in recognizing their own inner speech.
1117. Schizophrenia and fMRI Imaging
Dr. Sukhi Shergill discusses difficulties in recruiting schizophrenic patients for fMRI neuroimaging studies.
1112. Broca's Area - Primary Functions
Dr. Sukhi Shergill discusses the importance of Broca's area to generating speech.
1123. Schizophrenia - Risk Factors
Dr. Sukhi Shergill discusses some of the risk factors that can cause schizophrenia.
1244. Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobes contain a large number of substructures, whose functions include perception, face recognition, object recognition, memory, language, and emotion.
2121. Superior Temporal Gyrus
The superior temporal gyrus contain is responsible for processing sounds. It includes Wernicke's area, which is the major area involved in the comprehension of language.
2113. Occipital Lobe
The occipital cortex is the primary visual area of the brain. It has different groups of neurons that separately encode color, orientation, and motion information.